The level of technical knowledge required to read the article: ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (low)
Parties and their general responsibilities.
When the Customer and the Developer agree on the development of the project, the employees of both parties must unite in one whole team to achieve their mutual Project goal hand in hand.
Each party involved in the development of the project, usually those will be two parties - the Customer and the Developer, have their own set of responsibilities. Within these sets, specific tasks are then defined and assigned to the responsible individuals who make up the project team.
The general responsibilities of the parties are divided as follows:
| Customer’s side | Developer’s side |
|---|---|
|
|
Project team
In the context of the project, both the Customer and the Developer sides are one team. It is a partnership between all involved, where each member fulfills a specific role or several of them.
The following roles are most common in IT projects:
- Project Sponsor
- Project Supervisor at management level
- Product Owner
- Project Manager on the Customer side
- Business Analyst
- System Analyst
- Project Manager on the Developer side
- Scrum Master
- UX Designer and UI Designer
- Chief Development Engineer
- System Architect
- Development Engineers or Programmers
- QA Engineers
- Testers
- End Users
- Stakeholders
Each project will have its own structure that will define the required roles. The team is created for the duration of the project and consists of members who actually implement the project and have tasks within the project. If necessary, in order to successfully complete the work, during the course of the project, the responsible persons may be changed or additional team members involved.
The figure shows the roles that make up the minimum and optimal project team required to implement the project. Permanent roles or the core of the project are depicted in green, roles that participate as necessary during the development process are shown in yellow, while basic communication directions are marked with lines.
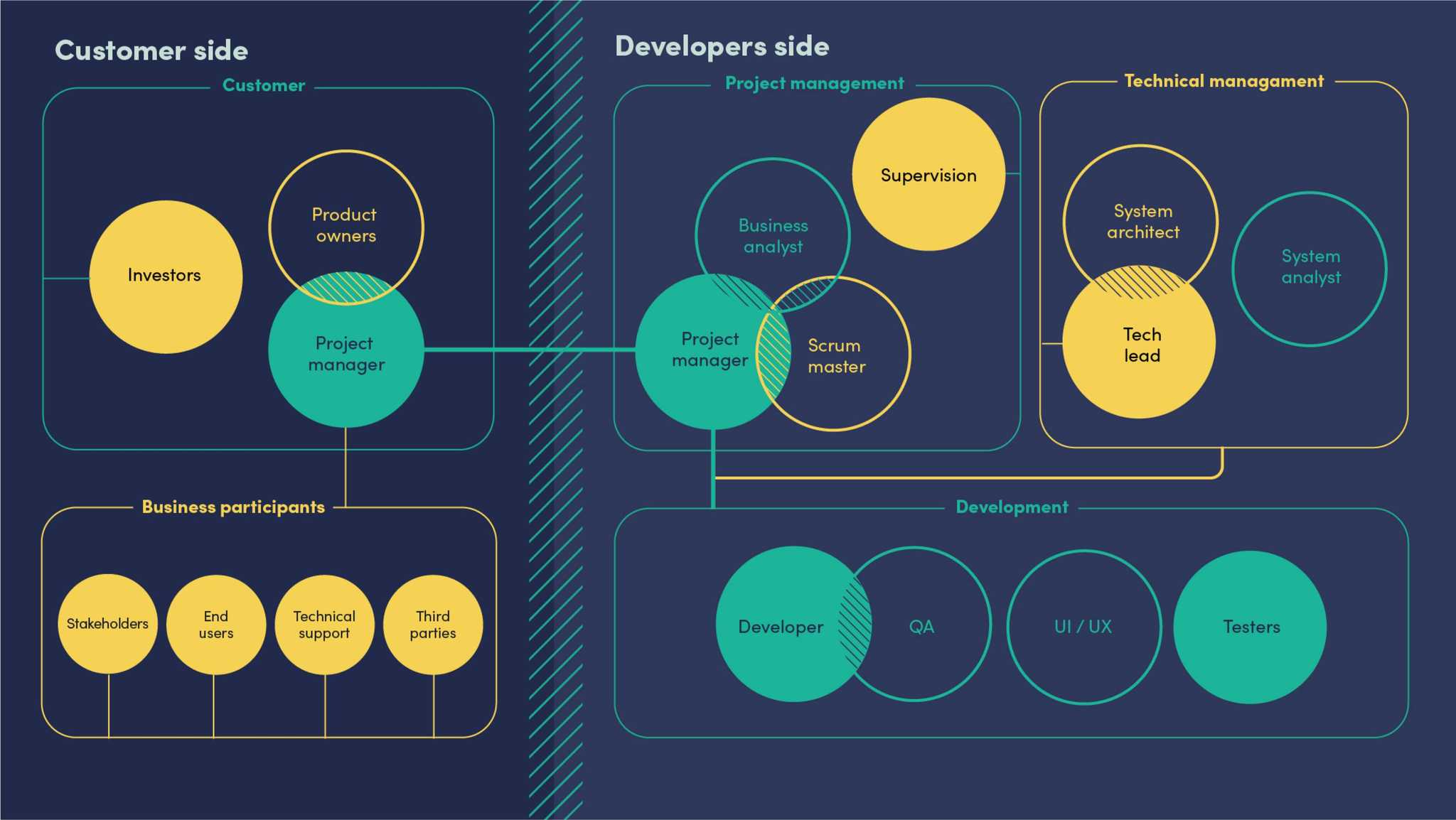
- Roles that form the core of the project team - without which you cannot make it. They actively participate in daily processes.
- Roles that connect to the project episodically: may not be present in the daily processes during project implementation, but are still necessary when reaching specific project milestones.
- Roles in addition to core roles in an optimal project structure. These roles, depending on the size and specifics of the project, often tend to be combined into one team member who covers the responsibilities of several roles, or overlap with other roles.
- show the directions of communication.
Role descriptions and responsibilities
Real life examples:
- The roles of Project Manager and Product Owner on the Customer side each have their own competences and responsibilities, but in fact both of these roles are performed by one person in the project, in consultation with the Project Sponsor if necessary.
- The project is technically specific, and on the Developer side, the roles of Business Analyst and System Analyst merge so much that both are undertaken by one person with the appropriate competence.
- On the Developer’s side, no roles of Chief Development Engineer or System Architect are allocated, however these roles de facto are filled by other members of the team involved in the daily development processes. They take responsibility for the technological direction and code quality and, when necessary, consult with colleagues who do not participate in the project themselves.
- The Customer is a start-up with two members who both are the Project Owners and the Product Owners, both test the delivered solutions, both manage the project - one is more responsible for the legal side, the other - technical side of the project. Two members manage the full spectrum of team roles on the Customer side.
- Defining the business requirements of the project should be the Customer’s responsibility, however, based on experience and competences, the Developer helps to define them, so that the final result meets the requirements of the real End Users as much as possible. (You can read more about the feasibility study here)
IT projects are as varied and interesting as the life itself, so the roles described in theory often merge, overlap and complement each other. Team members' previous experience, skills, and above all - mutual communication are of great importance here.
Below, it is possible to get acquainted with the classic division of responsibility and duties by roles in more detail.
Roles on the Customer side
Project Sponsor
The Project Sponsor is often also the author of the idea of the project or the one who defines the goal of the project implementation. The Project Sponsor is also the one who decides on the allocation of resources for the execution of the project and is the main decision maker.
Product Owner
The Product Owner is the representative of the Customer who is responsible for the product created as the result of the project. Their key responsibilities:
- Defining requirements;
- Ensuring communication with Developer’s representatives, participating in regular meetings and answering developers' questions, providing necessary information;
- Project scope related decision making.
Project Manager on the Customer side
In practice, often overlaps with the role of Product Owner.
Key responsibilities:
- Ensuring communication with the Developer's representatives. Participating in regular meetings and answering developers' questions, providing necessary information;
- Project scope related decision making (deadlines, budget, order of priorities, change management), participating in regular meetings and answering developers’ questions, providing necessary information;
- Providing the environment in which the software is to be installed;
- Communication with third parties;
- Providing the Developer with the data necessary for testing;
- Providing the resources necessary for system testing and managing the testing processes both during delivering the whole project as well as separate tasks;
- Management of the project delivery-acceptance procedure.
End Users
End Users are those who will actually use the system developed. It is important to involve these people in the defining of the requirements, as well as during development and testing phases of the project.
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are those with a direct interest in the project outcome: company management, strategic partners, legislators, competitors, etc.
Roles on the Developer side
Project Supervision at management level
Responsibilities:
- Supervising the project implementation at a strategic level;
- If necessary, getting involved in the resolution of conflict situations among the representatives of the Parties.
Project Manager on the Developer side
The Project Manager on the Developer side is like a bridge between the Customer and the development team. The Project Manager is the one who is responsible for the "who, what, where, when and why" of the project plan and who follows up to ensure that the project objectives are achieved.
Key responsibilities:
- Overseeing the project scope (deadlines, budget, priorities);
- Defining the project development time plan;
- Defining the communication plan;
- Project resource management;
- Distribution of tasks within the team;
- Performance analysis of the developers;
- Change management;
- Risk management;
- Making the meeting notes;
- Preparing status reports;
- Managing the procedure of project delivering.
Scrum Master
When working within the Scrum framework of the Agile methodology, one of the roles on the Developer side is the Scrum Master.
Key responsibilities:
- Monitoring that the Scrum guidelines are followed over the course of work;
- Eliminating blockers of performing the tasks;
- Planning project meetings;
- Providing support to the Product Owner in defining requirements and tasks.
In practice, even without specifically using the Scrum framework, the responsibilities typical of this role tend to be undertaken by the Project Manager.
UX Designer and UI Designer
Key responsibilities:
- Analyzing functional requirements defined by the Customer;
- User research, surveys;
- Defining the architecture of the solution (UX), optimising it;
- Development of system visual prototypes;
- Usability testing;
- Defining the visual guidelines (UI) of the system;
- Documenting design-related decisions.
The focus of UI design is the user interface: graphic design, content formatting, stylistics. Responsible for how the system looks.
The main task of UX design is to provide a seamless user experience using the system that is being developed. UX designers analyze user behavior and expectations about system operation, creating an easy-to-understand application architecture. Responsible for how easy it is to use the system.
You can read more about the design development processes here.
Business Analyst
A Business Analyst is responsible for translating business needs into requirements and documenting them appropriately before development begins.
Key responsibilities:
- Research and analysis of business processes;
- Compilation, formalization and coordination of requirements with the Customer;
- Development of proposals for necessary changes in existing or planned processes;
- Development of documentation.
System Analyst
The primary focus of this role is translating business requirements into technical requirements for developers, creating the most appropriate technical design for the system.
In practice, often overlaps with the roles of Business Analyst and System Architect.
Chief Development Engineer
A bridge between the Development team and the Project Manager and/or Business Analyst, providing technical direction for the project.
System Architect
Main responsibilities: defining the technical and functional architecture of the system.
In practice, often overlaps with the roles of System Analyst and Chief Development Engineer.
Development Engineers or Programmers (Back-End, Front-End)
Key responsibilities:
- Development and implementation of the project according to the defined requirements and competences;
- Progress documentation;
- Estimation of the tasks.
The Front-End Programmer works on the visible part of the project, ensuring smooth communication of the interface and business logic.
The Back-End Programmer works on the implementation of business logic on the server side, which is invisible to the customer.
QA Engineer
Key responsibilities:
- Development of system performance, regression and other automated tests;
- Performing code review.
Tester
Key responsibilities:
- Analysis of development requirements;
- Defining test scenarios;
- Manual testing and registration of detected errors.

