AI's gone from mystery novel to something real and accessible to regular people (not engineers). And it of course happened when a few companies rolled out Generative AI tools. Now AI can ‘talk’ to us… in our language.
We want to share an “AI terminology starter pack” so that it would be easier for you to navigate the AI landscape and terminology. The core idea of this article is to simplify AI complexities, and aim to align expectations with reality, allowing both technical and non-technical individuals to discuss AI's societal impact with clarity.
A frequent challenge is using the terms. Let’s clarify the basics using the terms-map (above) and concise definitions Please keep in mind that true AI landscape is a lot more stuffed with different terms and concepts. Here is our shortlist:
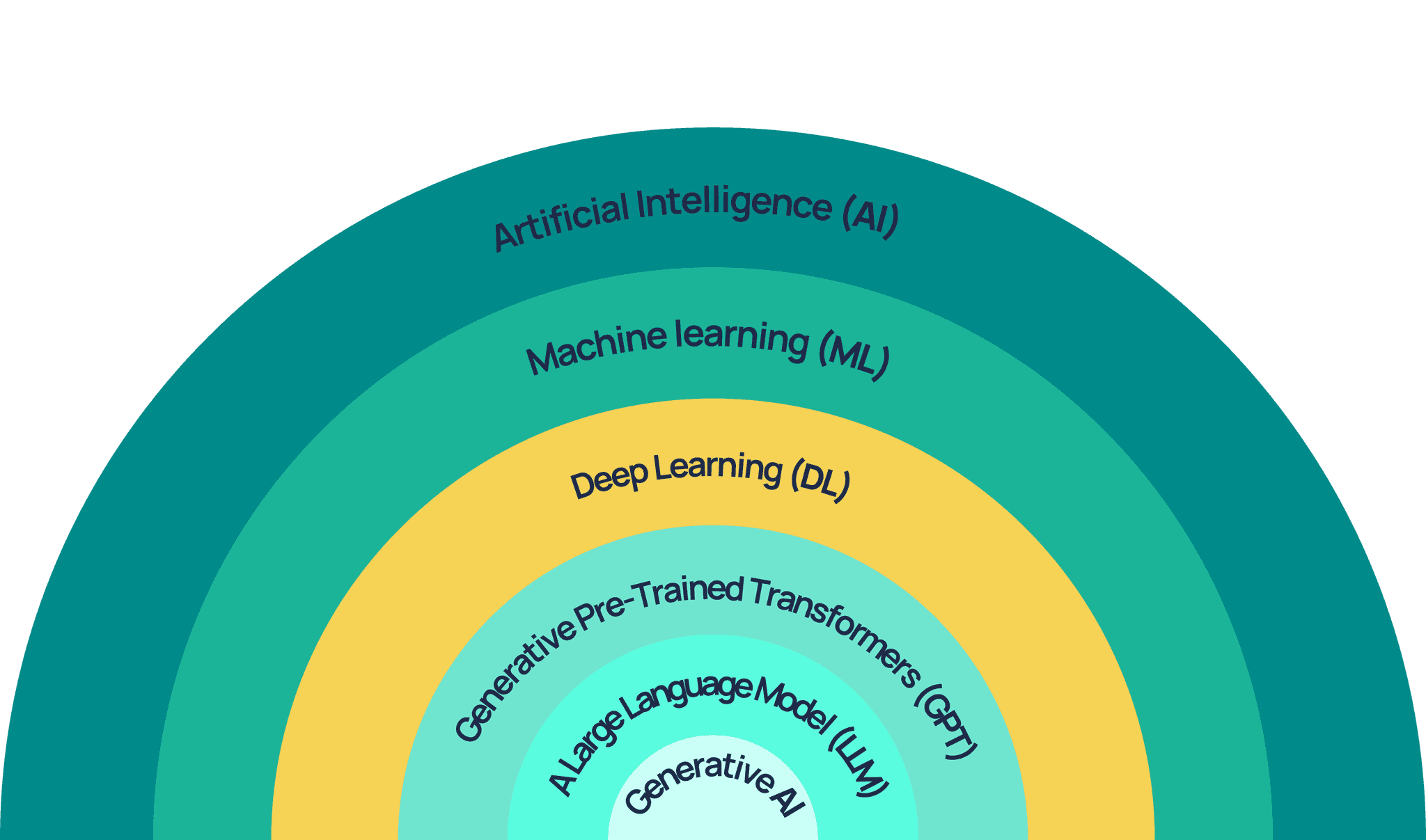
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI refers to machines' ability to exhibit intelligence, in contrast to the natural intelligence shown by humans or animals. Simply put, it's how machines can learn, reason, and draw conclusions.
Machine learning (ML):
Machine learning is a subset of AI that uses data and algorithms to mimic human learning, refining its precision over time.
The algorithm learns from specific data where the expected results are pre-labeled. It's often used for tasks like sorting items (like detecting spam) or forecasting values (such as estimating software quote).
Unsupervised Learning:
The algorithm processes data without predefined labels to uncover hidden patterns. Typical uses involve grouping similar items (like segmenting customers) or finding relationships (like analyzing golfers score for the next round).
Reinforcement Learning:
The algorithm adapts by engaging with its surroundings and gets feedback through rewards or penalties. This approach is common in fields like robotics, video games, and specific optimization challenges.
Few-Shot and Zero-Shot Learning:
Methods that train models to identify patterns or decide with minimal examples, and in some cases, like zero-shot learning, without any direct examples at all.
Artificial Intelligence (AI):
AI refers to machines' ability to exhibit intelligence, in contrast to the natural intelligence shown by humans or animals. Simply put, it's how machines can learn, reason, and draw conclusions.
Deep Learning (DL):
Belongs to a wider group of ML techniques, characterized by layered algorithms forming "artificial neural networks." These algorithms can independently learn and make smart choices, mirroring human brain functions.
Generative AI (GenAI):
Refers to specific DL models that learn from their input data and subsequently produce high-quality text, images, and similar content.
Generative Pre-Trained Transformers (GPT):
Is a type of GenAI models that use advanced transformer structures, known for detecting distant connections and understanding context in data sequences.
A Large Language Model (LLM):
Is a GPT algorithm (not a knowledge database) skilled in identifying, summarizing, translating, forecasting, and producing text or other content, drawing on insights from extensive datasets.
Another quite a popular expressions you will hear are:
- Traditional AI
- Generative AI
Traditional AI mainly analyzes data and predicts outcomes, whereas generative AI not only does that but also is able to produce new data resembling what it was trained on.
At Mitigate, we're convinced AI will transform how we use technology. We highly recommend you to grasp the basics, helping you spot AI opportunities within your organization.